When we talk about artificial selection, many people wonder what it really means and why it matters. Simply put, artificial selection is another name for selective breeding, a process in which humans intentionally choose which plants or animals reproduce to emphasize certain desirable traits.
Unlike natural selection, which is driven by environmental pressures and survival of the fittest, artificial selection is human-directed.
People search for this term because it is a cornerstone concept in biology, genetics, and agriculture. Understanding it helps explain how humans have shaped the plants and animals around us, everything from crops that feed millions to the pets in our homes.
This guide will explore artificial selection in detail, including its meaning, history, examples, advantages, disadvantages, and significance in today’s world.
What Is Artificial Selection? 🤔
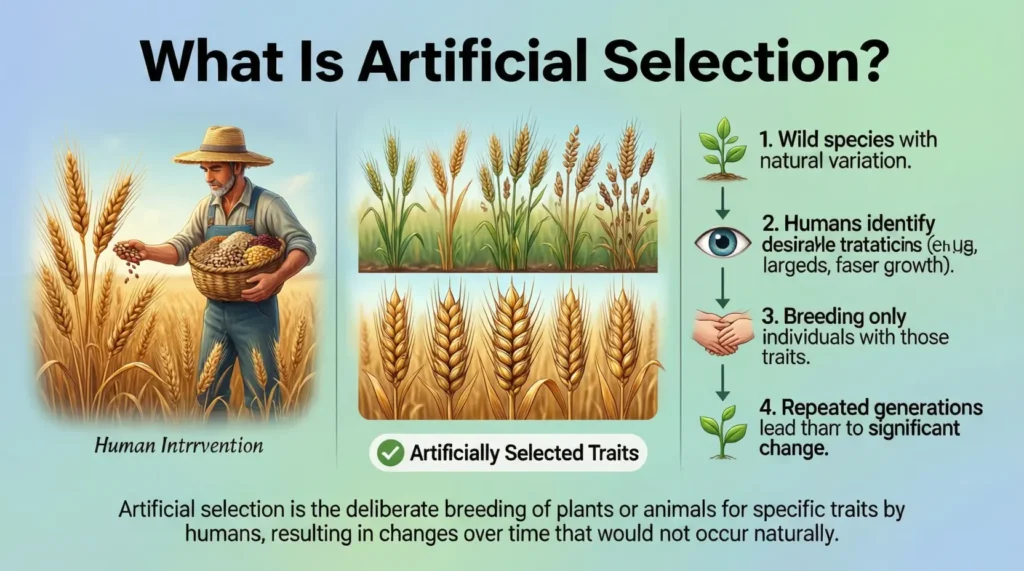
Artificial selection, also called selective breeding, is the practice of breeding organisms with specific traits to produce offspring that share those traits. Humans pick parents based on characteristics such as size, color, productivity, or behavior.
- Example: Farmers breeding cows that produce more milk.
- Example: Dog breeders selecting the cutest or most obedient dogs.
The key idea is that humans are directly controlling evolution for their benefit, rather than leaving it up to nature.
History of Artificial Selection 🏛️
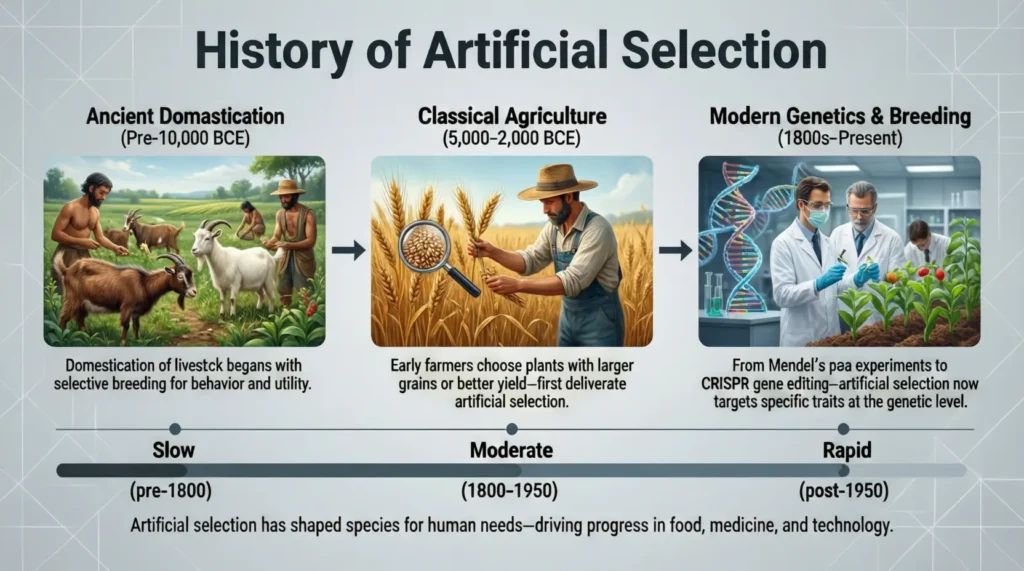
Artificial selection is not new. Humans have been practicing it for thousands of years.
- Ancient agriculture: Early farmers selected seeds from the best crops to plant the next season.
- Domestication of animals: Wolves were bred into various dog breeds over thousands of years.
- Modern examples: Laboratory experiments in genetics often use selective breeding to study inherited traits.
This long history shows how artificial selection has shaped human civilization, from food production to companionship.
How Artificial Selection Works ⚙️
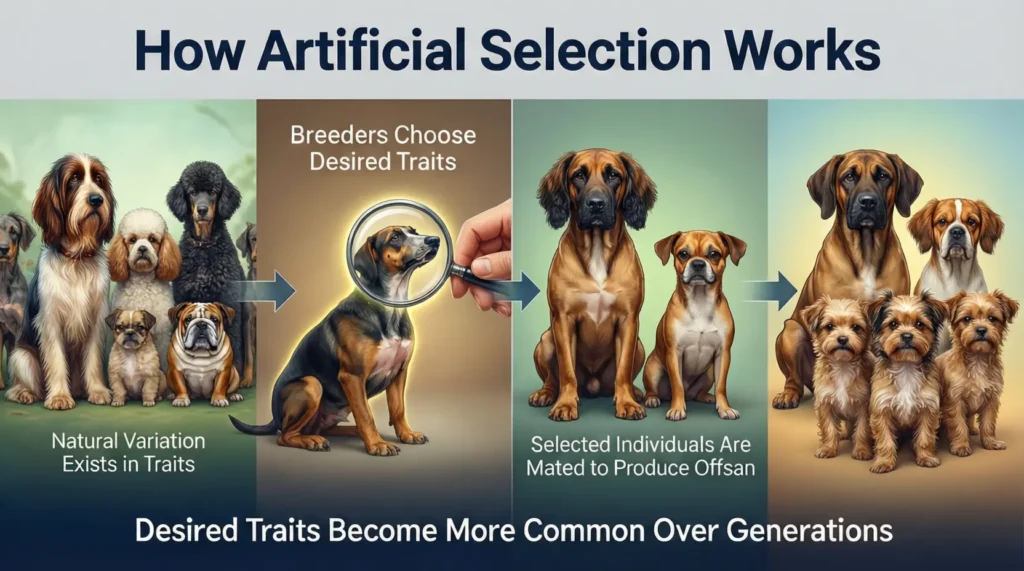
Artificial selection involves several steps:
- Identify a trait: Choose a characteristic you want to enhance (e.g., bigger fruits, faster horses).
- Select parents: Pick organisms with the best traits.
- Breed them: Allow them to reproduce.
- Evaluate offspring: Keep those with the desired traits for further breeding.
- Repeat: Over generations, the trait becomes more pronounced.
This process is gradual but powerful, allowing humans to shape species in ways that natural selection might never achieve.
Types of Artificial Selection 🧬
There are different ways humans can practice artificial selection:
- Positive selection: Encouraging traits we like.
- Example: Breeding cows with high milk yield.
- Example: Breeding cows with high milk yield.
- Negative selection: Discouraging undesirable traits.
- Example: Avoiding dogs prone to genetic diseases.
- Example: Avoiding dogs prone to genetic diseases.
- Hybridization: Combining traits from different varieties.
- Example: Cross-breeding plants for pest resistance.
- Example: Cross-breeding plants for pest resistance.
Each method serves a specific purpose, depending on the desired outcome.
Examples of Artificial Selection in Animals 🐶
Artificial selection has produced many animal breeds that we see today:
- Dogs: From tiny Chihuahuas to massive Great Danes.
- Cats: Breeds like Siamese or Persian cats.
- Cattle: Dairy cows vs. beef cows.
- Horses: Racing Thoroughbreds vs. working draft horses.
- Chickens: Egg-laying hens or meat-producing breeds.
Humans have shaped these species to meet specific needs, whether for companionship, work, or food production.
Examples of Artificial Selection in Plants 🌾
Plants are also heavily influenced by artificial selection:
- Wheat: Bred for higher yield and disease resistance.
- Corn (maize): Larger cobs and kernels through selective breeding.
- Tomatoes: Improved taste, size, and color.
- Rice: Drought-resistant or high-yield varieties.
- Apples: Many varieties like Gala, Fuji, and Honeycrisp.
These examples show how selective breeding can improve food quality, quantity, and sustainability.
Differences Between Artificial and Natural Selection 🔄
While both processes affect which traits survive, there are key differences:
| Feature | Artificial Selection | Natural Selection |
| Driven by | Humans | Environment |
| Goal | Specific traits | Survival and reproduction |
| Speed | Faster, targeted | Slower, gradual |
| Example | Dog breeds, crops | Camouflage in animals |
Understanding this difference is crucial for biology students and researchers.
Advantages of Artificial Selection 🌟
Artificial selection offers many benefits:
- Improved food production – Higher yield crops feed more people.
- Better animal breeds – Healthier, more productive livestock.
- Aesthetic purposes – Beautiful pets and ornamental plants.
- Scientific research – Helps study genetics and evolution.
- Customization – Tailored traits for human needs.
These advantages have made artificial selection a cornerstone of agriculture and domestication.
Disadvantages of Artificial Selection ⚠️
Despite its benefits, there are also downsides:
- Reduced genetic diversity – Inbreeding can cause health problems.
- Unintended consequences – Traits can cause weaknesses.
- Ethical concerns – Manipulating life for human purposes raises moral questions.
- Dependency – Over-reliance on human selection may weaken natural adaptability.
- Environmental impact – Monocultures can harm ecosystems.
Balancing benefits and risks is essential for sustainable practices.
Artificial Selection in Modern Science 🔬
Today, artificial selection is still widely used:
- Laboratory research: Studying disease resistance in animals.
- Agriculture: Creating high-yield or pest-resistant crops.
- Conservation biology: Breeding endangered species to increase population numbers.
Even with advances in genetic engineering, traditional selective breeding remains valuable for many purposes.
Why Understanding Artificial Selection Matters 📚
Learning about artificial selection helps us:
- Appreciate the origins of modern plants and animals.
- Understand human influence on evolution.
- Make informed decisions about agriculture and animal breeding.
- Discuss ethical issues in biotechnology and genetic research.
It’s a concept that connects biology, history, and everyday life.
Conclusion:
Artificial selection, another name for selective breeding, has shaped the plants and animals around us for thousands of years. From adorable pets to high-yield crops, humans have guided evolution to meet specific needs.
Understanding its methods, advantages, disadvantages, and examples allows us to appreciate both the power and responsibility that come with shaping life.
If you’re a student, farmer, or science enthusiast, learning about artificial selection highlights the fascinating intersection of nature and human creativity.

I am a celebrated American author known for my straightforward yet powerful use of English. My writing combines simple vocabulary with strong emotional impact, making me an excellent reference for understanding word choice, tone, and clarity in English writing.










